


Recently, the research team led by Prof. XU Chao,in cooperation with Prof. GUANG Shouhong, both from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), revealed the composition mechanism of the nematode Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNA) biogenesis and chromosome segregation (PICS) complex and the molecular mechanism that regulates PICS. The results were supported by the data of in vitro biochemical experiments. Besides, the mutation experiment verified that the PICS subunit interaction interface residues play an important role in the formation of the complex. This work was published on Nature Communications.
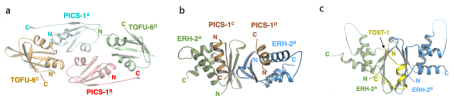
Structure diagram of 3 subcomplexes in PICS (Image by WANG Xiaoyang et al.)
Furthermore, based on genetics, cell biology and imaging experiments, the amino acid mutations in the important interface of the PICS complex were obtained. Researchers also found that the intracellular localization of the subunits of the PICS complex depended on each other. The defect in the composition of the PICS complex not only affects the formation of the complex and its intracellular granule localization, but also reduces the level of mature piRNA and leads to abnormal mitosis and chromosome segregation.

a. PICS complex subunit interaction network diagram; b. PICS complex action model. (Image by WANG Xiaoyang et al.)
(Written by WENG Jingwen, edited by LI Xiaoxi, USTC News Center)
 Back
Back