


There are two main types of cells in the human brain: neuron cells and glial cells. Neuron cells are responsible for receiving stimulations, generating excitements and transmitting information in the form of nerve impulses, while glial cells mainly support neurons through substance metabolism.
Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) is secreted mainly by glial cells and then delivered to neuron cells. It is one of the most abundant apolipoproteins in the brain and the greatest risk factor for Alzheimer's disease, but the causative mechanism has been unclear.
The mechanism how ApoE reprograms neuronal cholesterol metabolism and the impact of the metabolic regulation on neuronal functions, especially learning and memory processes, has been revealed, indicating a novel mechanism by which ApoE4 causes Alzheimer's disease.
This work, conducted by Prof. LIU Qiang’s team from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), was published on Neuron.
Researchers found that the transmission of ApoE could not only provide nutrition but also improve neuron’s information conveyance ability by suppressing its own anabolic pathway.
ApoE significantly inhibited key enzymes in the cholesterol synthesis pathway in neurons, thereby inhibiting cholesterol anabolism in neurons. This helps increasing the acetylation level of histones, which is related to the realization of cognitive functions, such as learning memory.
Further studies revealed that the metabolic regulation is dependent on the miRNAs carried by ApoE. Moreover, via gene transcription and epigenetic analysis, researchers found that the ApoE-mediated metabolic and epigenetic regulation of neurons exhibited significant subtype specificity. The ability of ApoE4 to regulate neuronal cholesterol metabolism and epigenetics was significantly weaker than that of ApoE3.
This study reveals a novel function of ApoE in the brain and elucidates a new mechanism by which glial cell-derived ApoE affects learning memory. Besides, it also reveals how ApoE4 is involved in the pathological process of Alzheimer's disease, which has important implications for an in-depth understanding of the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.
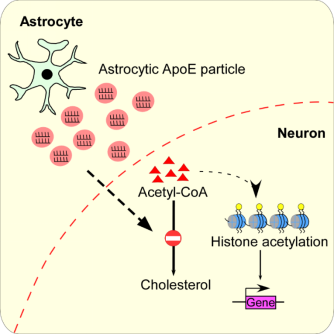
Schema of ApoE's regulation on neuronal cholesterol metabolism and epigenetics (Image plotted on Neuron)
Paper link:
https://www.cell.com/neuron/fulltext/S0896-6273(21)00005-2
(Written by ZHANG Boxian, edited by JIANG Pengcen, USTC News Center)
 Back
Back